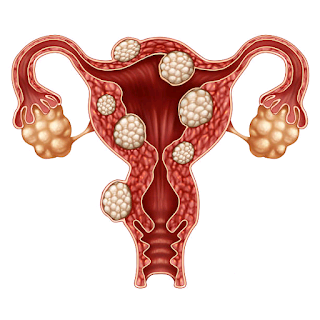
Fibroids are growth of tumor that are made up of smooth muscle tissues, and fibrous connective tissues developed from the wall of the uterus.
 |
| Source: Evergreen Women's Health, PC. |
According to estimation, 80% to 90% of women will develop fibroid during their lifetime.
However, many women will not experience any symptoms, due to this, they do not know they have fibroid, and this normally happens when the size of the fibroid is small (an asymptomatic, they did not come with unusual pain)
One of the characteristics of fibroid is that they are not cancerous (benign). Although there are fibroid that begins as cancer but in most cases they are very rare, and because of this it is highly recommended for women to check in with the doctor For observation.
What are the causes of fibroid?
The cause of fibroid are not known there's no definite answer as to what causes fibroid, but happens mostly in women of reproductive age.
Who is at risk of having fibroid?
Although fibroid is a common growth that develop in the pelvis, but there are factors that can increase the chances of developing it,
And this are;
- Obesity: Women who are overweight has and higher chance of developing fibroid.
- Age: As women age, the age of 30's and 40's up to menopause, there's a chance of having fibroid.
- Family history of fibroid: This is due to genetic component transferred from mother to daughter. If a mother has fibroid, there's a chance her daughter will develop it also.
What are the symptoms of fibroid?
Most women will not experience any symptoms, However fibroid of larger size can come with the following symptoms;
- Pelvic pain and pressure
- Difficulty in getting pregnant
- Pain during intercourse
- Prolonged periods
- Low back pain
- Frequent urination
- Increased abdominal enlargement
The types of fibroids are determined by their location in and on on the uterus, and how they are attached.
These includes;
- Intramural fibroid: They are the ones that are embedded into the wall of the uterus.
- Subserosal fibroid: They are the most common fibroids, They can grow large at times, and push outside of the uterus to the pelvis. They are located outside of the uterus.
- Submucosal fibroid: This type of fibroid grow inside the uterus cavity where a baby grows during pregnancy.
- Pendiculated fibroid: this type is located on the outside of the uterus, connected to the uterus with a stem (usually thin) they are stuck like and also have a wider top, often described as the mushroom like fibroid.
In most cases fibroids are detected during pelvic exam.
There are numerous steps that can be carried out to confirm whether or not a woman has fibroid, and these includes;
- Laparoscopy: ln this test a small cut would be made in the lower abdomen, and a tube usually with a flexible and thin camera on the end will be inserted into the abdomen to closely look at the internal organ.
- Hysteroscopy: A test of a thin flexible tube with a camera on the top is inserted into the vagina and cervix to observe the uterus.
- Ultrasonography: This is the making use of sound waves to create a picture of the internal organs. This type of test may be conducted by transabdominal route or trans vaginal route depending on the size of the uterus.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): This test create detailed images of the internal organs by using magnets and radio waves.
The treatment of fibroid varies depending on the size, location, numbers and symptoms.
- if the pelvic exam shows it is small in size and no symptoms is experienced, it may not need treatment, However in such cases it should be monitored closely from time to time.
- If the fibroid comes with symptoms treatment is highly recommended.
Treatment options for fibroid includes;
- Iron supplements
- Birth control
- Over the counter pain medication Oral therapies
- Surgery
Can fibroid be prevented?
No, the risk of developing it can be reduced.
Fibroid and pregnancy
Can a woman get pregnant if she has fibroid?
yes, but after conception such a woman has to work with the healthcare women so as to develop a monitoring plan for the fibroid.
Will fibroid go away on their own without treatment?
Yes, fibroid can shrink away in some women after menopause, this is due to the decrease in the hormone produced in the body of women after menopause.
Consult your healthcare if you experience unusual pain or discomfort of any kind.
Fibroid can be treated or cured.
